HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
The real-world data are used in drug authorization procedures, comparative efficacy and safety research, to make changes in the Summary of Product Characteristics, clinical recommendations. One more aspect where RWD/RWE can be used is the health technology assessment. Although there is a clear need for high-quality recommendations regarding RWE studies, published today documents do not contain clear instructions.
METHODOLOGY
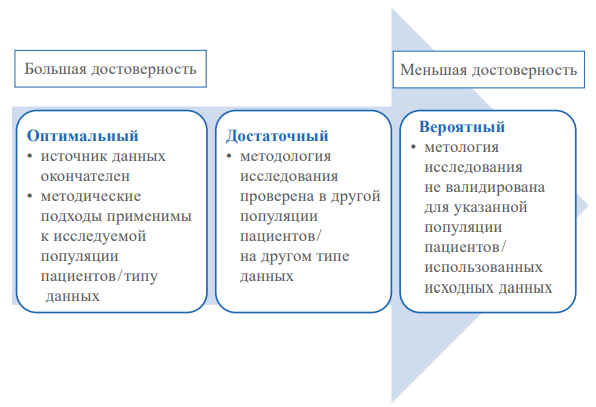
Recently, the development of a methodology for obtaining evidence of clinical efficacy and safety of medical technologies based on the collection and analysis of real clinical practice data (real-world data; RWD; real-world evidence; RWE) has become extremely relevant. Different types of research are used in RWD/RWE. It must develop a unified methodology for conducting and approach the reliability of the results of such studies. One of these approaches is the ranking of the reliability of research results based on an assessment of the quality of the original data: patient populations, exposures, outcomes and confounding factors (interfering factors). Simultaneously, for an optimal assessment of reliability, the following should be considered: a description of the data sources implemented during the study; techniques used to transform them; the techniques used to make up for missing information in the collection of these data.
The International Society of Pharmacoepidemiology (ISPE) and the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) have created a joint task force, including representatives of key international stakeholders, to create a coordinated protocol template for RWE studies that assess the effect of treatment and is designed to inform decision-making. The template is based on existing transparency efforts and includes the state-of-art ideas regarding the level of detail required to ensure reproducibility of the RWE study. The underlying principle was to achieve sufficient clarity regarding research data, design, analysis and implementation to achieve the three main objectives. Firstly, to help researchers carefully consider and document the choice and justification of the key parameters of the study, secondly, to facilitate decision-making by allowing reviewers to easily assess potential bias associated with the choice, and thirdly, to ensure research reproducibility.
INTERNATIONAL EXPERIENCE
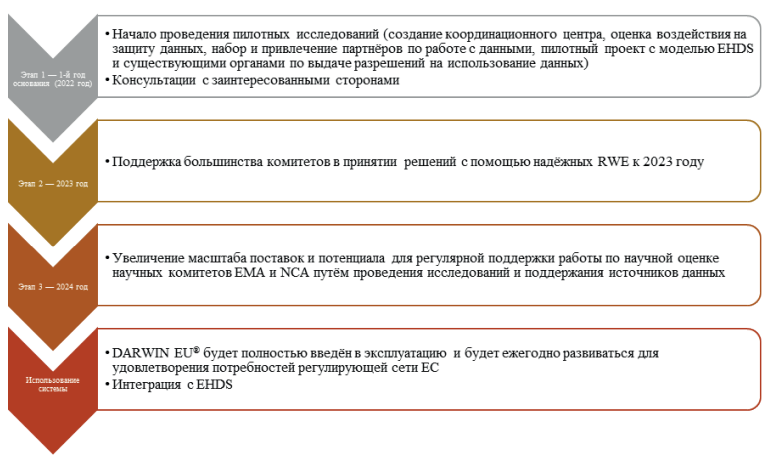
The growing volume and complexity of data that is currently being collected in a variety of settings and devices is of varying degrees and quality, posing a challenge for the public health sector to develop a robust electronic system that can be collected, analyzed and made available to clinicians. The creation of a system, the development of the capabilities and potential of information technologies for obtaining, managing and analyzing a large amount of data, will allow to identify facts regarding the safety and effectiveness of the use of drugs, to investigate the validity of statements made by pharmaceutical companies, to obtain a more accurate characterization of treatment methods in individual healthcare sectors and to provide doctors with quick and constant access to this information, which will facilitate its use in the treatment of patients. The development of such a tool is a priority for the health care system in a changing world. An example of such a tool is the Data Analysis and Real Word Interrogation Network (DARWIN EU®), which was launched on February 9, 2022 by the European Medicines Agency. The purpose of this article is to review the history of creation, organizational structure, operating principles, current experience of the European Union regulatory network and comparison with the experience of international regulatory bodies. The article, along with the experience of the European Medicines Agency, also considers similar initiatives in the US and Canada.
This article provides a brief overview of the key aspects of planning, conducting, and reporting NICE clinical practice data collection and analysis studies, as well as general information about the sources of real-world data (RWD) and their use in NICE management decision-making algorithms. The difficulties of finding and using RWD are described, as well as methods for overcoming them, brief NICE recommendations for assessing the suitability of data and an algorithm for conducting quantitative studies to collect evidence from RWD are given.