INTERNATIONAL EXPERIENCE
About 10 years ago, the FDA launched an initiative to expand the role of patients in informing regulators and sponsors about the most serious consequences of the disease and the main treatment goals that can lead to desired medical outcomes. This initiative has grown into four guidance that aim.
This article describes regulatory approaches to the decentralized clinical trials (in whole or in part) in international practice, as well as in the Russian Federation and the Eurasian Economic Union.
DRUG UTILIZATION RESEARCH
Pharmacoepidemiological studies are necessary to improve the system of rational use of drugs and to identify the most problematic areas. Such studies make it possible to evaluate not only quantitative indicators of consumption but also indicators such as patient adherence, frequency of cases of polypharmacy, and drug abuse.
HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
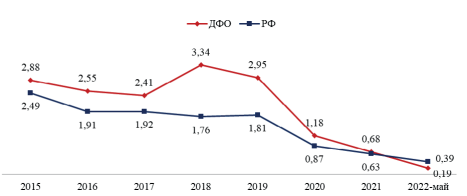
Meningococcal infection (MI) is one of the heaviest illnesses with specific clinical picture and outcomes. MI prophylaxis is also actual from a social-economic viewpoint. Analysis based on RWD is important and should include epidemiological, medical, regional economic parameters as well as demographic data.
Aim: economic evaluation of the potential outcomes of vaccination against MI in Far East Federal District of Russia (FER) in frames of vaccination growth in children.
Materials and methods: Modelling of epidemiological and economic outcomes of MI vaccination with MenACWY-D vaccine in 95% of 3-year-old children in FER. Economic model usage cost vaccination, its efficacy, morbidity after vaccine usage, and mortality with such kind of parameters comparison w/o vaccination. The economic gain of vaccination is calculated in terms of the prevented loss of life years and the monetary equivalent of the per capita domestic regional product.
Results: Vaccination against MI in 100 thousand children aged 3 years will decrease morbidity by 64,5% and mortality by 75% during 8 years after vaccination. Social gain is 5,8 mln RUR due to morbidity decrease and 1,3 bln RUR due to saving lives.
Conclusion: Vaccination has an economic advantage — benefit after 100 thousand children vaccination up to 4,3 times higher than cost of vaccination in FER.
DRUG SAFETY
Signal detection is a crucial step in the discovery of post-marketing adverse drug reactions. There is a growing interest in using routinely collected data to complement established spontaneous report analyses.
The aim. This work aims to systematically review the methods for drug safety signal detection using routinely collected healthcare data and their performance, both in general and for specific types of drugs and outcomes.
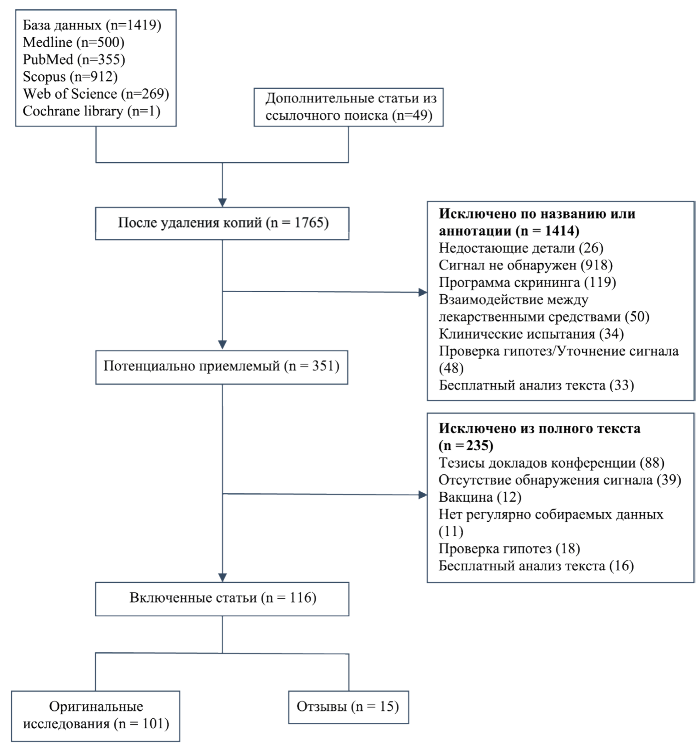
Metodology. We conducted a systematic review following the PRISMA guidelines, and registered a protocol in PROSPERO.
Results. The review included 101 articles, among which there were 39 methodological works, 25 performance assessment papers, and 24 observational studies. Methods included adaptations from those used with spontaneous reports, traditional epidemiological designs, methods specific to signal detection with real-world data. More recently, implementations of machine learning have been studied in the literature. Twenty-five studies evaluated method performances, 16 of them using the area under the curve (AUC) for a range of positive and negative controls as their main measure. Despite the likelihood that performance measurement could vary by drug-event pair, only 10 studies reported performance stratified by drugs and outcomes, in a heterogeneous manner. The replicability of the performance assessment results was limited due to lack of transparency in reporting and the lack of a gold standard reference set.