ACTUAL REVIEW
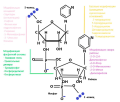
This review describes the basics of protein biosynthesis and RNA interference processes, discusses the useful and unique properties of siRNA therapy, its advantages and disadvantages in comparison with other gene silencing methods, provides a brief overview of technical advances and modifications of siRNA therapy, and characterizes siRNA-registered drugs and agents at different stages of clinical trials.
HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
Background. It has been done previously that the main expenditures in diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2T) not related with glycemia correction, but they are spending on the cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) of DM2T and indirect costs of CVDs in work-aged patients.
Objective. Modelling of potential clinical and economic results of effective programs for DM2T control realizations and their influence on CVDs and mortality in case of HbA1c targets reached.
Materials and methods. The Oxford UKPDS model has been used for epidemiologic and economic benefits in cases of decreased CVDs and premature deaths due to more effective control of DM2T. We created 48 cluster groups of patients based on age (less 40 y. o., 40–60 y. o., 60+ y. o.) and HbA1c levels and CVDs anamnesis. The probability of CVDs over 10 years was calculated for each cluster. Subsequently, DALY, YLL, and YLD have also been defined. Average salary, GDP per capita, etc. were used for the analysis.
Results. Successful control of DM2T can lead to saving 1.69 billion YLL, or 115.93 years per 100th of people annually. The prognosis for CVD morbidity and mortality decreasing due to more effective DM2T control can decrease DALY loss by 17 %. The effect on the Russian economy in this case can be evaluated as 197,8 billion RUR over 10 years (based on salary level). The benefit in the GDP per capita metric is higher — 213.6 billion RUR annually.
Conclusion. Effective methods of DM2T control can reduce the risk of CVD occurrence and progression; therefore, they are economically justified and can be considered as an additional source of budgetary benefits, leading to lower medical care costs.
DRUG SAFETY
Relevance. Off-label use of medications is a common practice in clinical settings. To address the growing interest in this issue, the International Society for Pharmacoepidemiology (ISPE) has developed new general guidelines for off-label prescribing in clinical practice that emphasize the importance of evidence-based medicine and promote transparent communication between healthcare professionals and patients.
Objective. The aim of this work was to analyze and present key trends for optimizing off-label prescribing decisions based on the ISPE recommendations (2023).
Results. The report highlights five main recommendations: seeking strong scientific evidence, including the use of real-world data; using expert knowledge to evaluate and summarize evidence; developing recommendations with rigorous consistency; aligning the use of off-label medications with research; and strengthening collaboration among regulators, researchers, clinicians, and the pharmaceutical industry.
Conclusions. A comprehensive approach is required to address the problem of off-label use of medicines. Implementation of these initiatives will reduce the risks associated with off-label use, generate sustainable scientific evidence, and improve the quality of patient care.
PRACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
The European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) has produced the very first expert-based guidance for reporting real-world evidence (RWE) studies specifically for oncology. The publication addresses nuances of modern RWE research in oncology and provides a comprehensive list of detailed key recommendations — that have also been transcribed into an interactive informative scoring checklist tool — for full article development in different RWE research scenarios.
ONCOLOGY
Background. Real-world data studies are an important source of knowledge on malignant tumors and their treatment. This knowledge is a tool for making decisions by health care professionals and patients. Regarding this, authors conducted literature search to identify real-world data studies published in the Russian scientific journals.
Objective. The study aim was finding and analyzing publications on real-world evidence studies in oncology therapeutic area.
Materials and methods. Full-text articles published in the Russian peer-reviewed medical scientific journals of 2022 and 2023 were systematically relieved and analyzed.
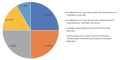
Results. 119 publications were selected. The following types of study data were identified: 1) data on patients management practice; 2) survival and other oncology outcomes regardless of treatment approach; 3) survival and other oncology outcomes depending on treatment approach; 4) efficacy of a concrete therapy; 5) treatment safety (toxicity) data; 6) clinical and demographic prognostic factors; 7) tumor (morphological, molecular and genetic) prognostic factors; 8) tumor characteristics (morphological, molecular and genetic) regardless of their prognostic significance; 9) oncology disease characteristic (e. g., comorbidities) regardless of its prognostic significance. The most common types of study data were the following: clinical and demographic prognostic factors — 24 studies; tumor (morphological, molecular and genetic) prognostic factors — 36 studies; tumor characteristics (morphological, molecular and genetic) regardless of their prognostic significance — 38 studies.
Conclusion. The modern real-world data studies in oncology therapeutic area are a very important source of knowledge on malignant tumors and their treatment.
BOOKSHELF
The European SocIn March 2024, the manual “Clinical and pharmacological characteristics of biotechnological drugs: from classifications to adverse events” was published under general ed. Kolbin A. S. This textbook discusses biotechnological drugs from the perspective of clinical pharmacology. Basic definitions and classifications are given. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and adverse events are reviewed. Examples of interactions between biotechnological drugs and small molecules are presented. A separate chapter examines the interchangeability of biological products — from basic terms and definitions of the concept of biosimilarity to regulatory aspects. The Appendix provides examples of clinical applications of therapeutic proteins. The manual is intended for students, residents, graduate students, clinical pharmacologists and physicians of other specialties.