INTERNATIONAL EXPERIENCE
Relevance. The regulation of orphan drugs plays a key role in the development of medicines for rare diseases that affect only a small percentage of the population. This specialized regulatory framework is designed to encourage pharmaceutical companies to allocate resources to the development of drugs for diseases that might otherwise be overlooked due to limited commercial appeal. Experts from Cogentia Healthcare Consulting Ltd. analyzed trends in the assessment of orphan drugs in the UK.
Objective. The aim of this work was to analyze and present the main trends in the optimization of decision-making regarding orphan drugs based on the data of an analysis conducted by the experts of Cogentia Healthcare Consulting Ltd.
Results. Regulatory bodies have shown some flexibility in the assessment of orphan drugs and have used approaches designed to address uncertainties in the evidence, accepting, in some cases, low-quality evidence, expert opinion and evidence from real-world clinical practice and applying more flexible pharmacoeconomic approaches. However, despite the existing assumptions, the evaluation process for orphan drugs often takes longer than that for non-orphan drugs.
Conclusions. Although different approaches to market regulation for orphan drugs have helped stimulate their development worldwide and address unmet medical needs, delays in decision-making for orphan drugs have seriously affected their availability to patients in need.
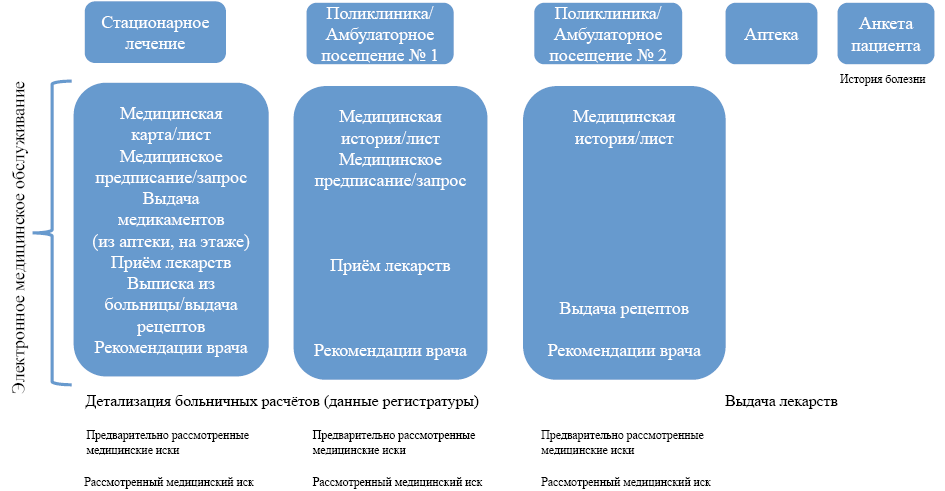
Real-word data obtained using medical devices differ from the use of drugs. When using medical devices, the effectiveness is usually not in doubt, and the issues of biocompatibility, safety, and long-term use come to the fore. This article presents a translation of the clinical guidelines of the People’s Republic of China on planning and conducting studies on the use of medical devices in real-world clinical practice, as well as statistical processing of the information obtained in an abbreviated form.
PRACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
There is currently no established framework for conceptualizing or implementing drug use. These recommendations provide a framework that outlines considerations to be considered when developing definitions of drug use in real-world clinical practice. The structure is intended to aid researchers in understanding and contextualizing the findings of pharmacoepidemiological studies.
MARKET
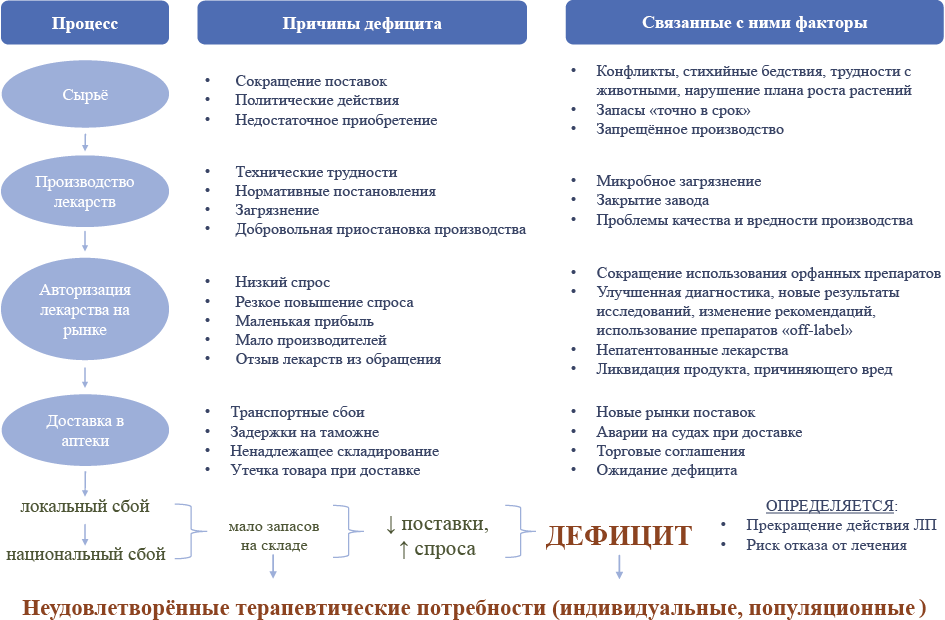
In recent years, the number of drug shortages has increased both locally and internationally. The sudden and unpredictable occurrence of drug shortages negatively affects the daily lives of healthcare workers and patients. Physicians are sometimes forced to prescribe alternative treatments considered less effective or even less well tolerated. These alternatives make it more difficult for patients to adhere to treatment and increase the risk of medication errors.
EDUCATION
Objective. Assessing the level of statistical literacy of medical students in the context of the transition from clinical medicine to evidence-based medicine and the increased need for doctors who can correctly interpret data presented in various scientific sources and conduct their own research.
Materials and methods. The research methods included an online survey and statistical processing of the results. Additionally, a business analysis service was used to validate the data and search for insights quickly. When statistically processing the results, descriptive statistics were used, and to compare indicators, non-parametric methods were used: Mann-Whitney and the Kruskal-Wallis test, which allow working with small samples, as well as one-way analysis of variance and correlation analysis. Confidence level of 0.05.
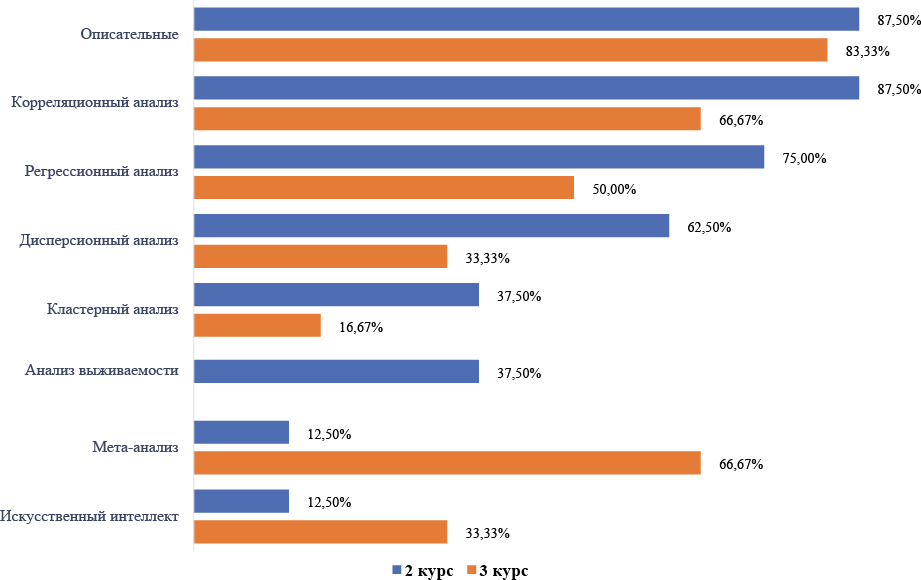
Results. Two hundred fifty-two respondents participated in the study. The study revealed that medical students, on average, had high grades in both the computer science course (4.5±0.6 points) and the statistics course (4.4±0.6 points). The level of statistical literacy is high immediately after completing the course but decreases over several years of study. There was a significant average positive correlation between teaching GPA and ICT scores (r=0.35, p< 0.05) and a significant weak positive correlation between teaching GPA and statistics (r=0.23, p< 0.05), and an average correlation between statistics scores and ICT (r=0.59, p< 0.05). More than half (54 %) of medical students wanted to undergo more in-depth training in the field of ICT, while 35 % of medical students wanted to study programing languages in depth, business analytics tools were in second place, and 49 % of students showed an interest in the in-depth study of statistics medical specialties.
Conclusion. There is a gap between students’ knowledge of statistics, computer science, and digitalization and the level of proficiency required of a specialist when entering the workforce. Its reduction is possible through students’ access to real clinical practice data throughout the entire learning process, the development of additional training programs dedicated to data analysis in medicine, and the development of a culture of working with data from the first year, including using business analytics tools and special attention focusing on competent data visualization.