A review of the literature concerning the efficacy and safety of combined anti-pseudomonas protected ureidopenicillin piperacillin/tazobactam usage. Randomized clinical trials and their meta-analysis have demonstrated that piperacillin/ tazobactam among non-carbapenem β-lactams is an equally effective alternative to carbapenems in the treatment of severe infections, including those caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing strains, regardless of the infection locus. It can be used in cases of carbapenem de-escalation if it is necessary. The use of this antimicrobial therapy strategy is justified not only from a clinical, but also from an economic point of view.
HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
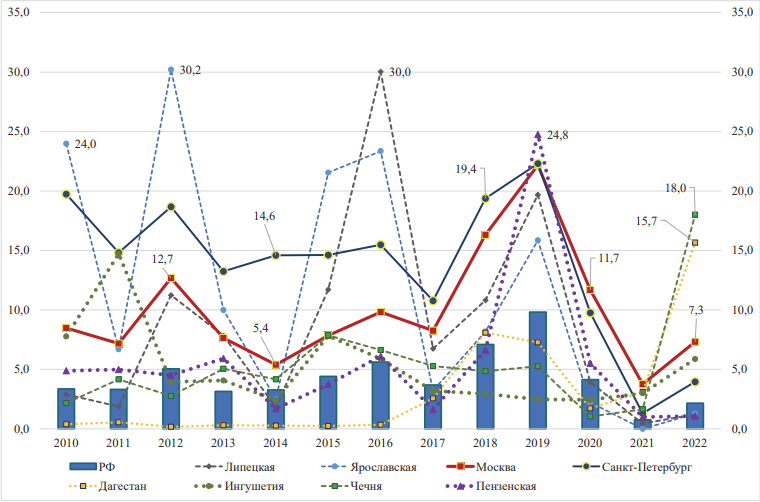
Actuality. Previously, we calculated the economic consequences of the booster vaccination against pertussis infection (CI) with the tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid and acellular pertussis vaccine, combined, adsorbed (INN) in some regions of the Russian Federation, which showed that the public benefit within 7 years after immunization could potentially exceed the cost of vaccination 1.23 times. At the same time, it is important to provide an economic justification for vaccination for a megalopolis, such as Moscow, with an underestimation of the diagnosis of the disease in conditions of high population density, contributing to the spread of infection. Materials and methods. The assessment of the economic benefits of obtaining an epidemiological gain during revaccination was carried out within the framework of a market economy using an assessment of the cost of the disease. The calculations were based on data on the cost of CI treatment in Moscow, considering cases of complicated and mild course and on the basis of current tariffs of the OMI system. Modeling was performed based on morbidity rates, taking into account the underestimation of detectability in a cohort of 14-year-olds numbering 100 thousand people. Two scenarios were compared, providing for the preservation of the existing procedure of revaccination only at 6 years (95% coverage) and the scenario in which the second revaccination of all adolescents was carried out at 14 years. Using the model, epidemiological indicators of changes in the incidence of CI were determined, and direct and indirect costs were calculated on their basis. When testing the sensitivity of the model, other levels of vaccination of 14-year-old children were also used in the calculations. Results. Booster revaccination of a conditional cohort of 100,000 children aged 14 years with the mentioned vaccine will reduce the incidence of pertussis during the period of saving immune protection (7 years) by 53.7% (from 1702.5 to 788.4 cases per 100 thousand of the population of these ages). This epidemiological gain will be accompanied by an economic benefit calculated in the metric of the total cost of prevented cases of the disease, which will amount to 155.4 million rubles. For a cohort of 100 thousand revaccinated adolescents of 14 years. The economic benefits accompanying a potential reduction in the incidence of infants can range from 254.4 to 470.5 million rubles, depending on the nature and intensity of contacts between adolescents and younger children. Conclusion. With the given parameters of underestimating the diagnosis and cost of the vaccine in the population over 14 years of age in Moscow, revaccination of adolescents is an economically justified measure.
INTERNATIONAL EXPERIENCE
Real-world data and real-world evidence play an increasingly important role in clinical research and healthcare decisionmaking. To use data and generate robust evidence effectively, they must be clearly defined and structured, semantically compatible and harmonized among stakeholders. On June 30, 2023, the International Council on Harmonization (ICH) presented for discussion a reflection paper on “International Harmonisation of Real-World Evidence Terminology and Convergence of General Principles Regarding Planning and Reporting of Studies Using Real-World Data, with a Focus on Effectiveness of Medicines”, which outlines their approach to achieve international integration in this area. This article provides an overview of the key aspects of the strategic plan proposed by the ICH.
In 2021, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued draft guidance on the use of electronic health records and medical claims data for regulatory decisions. The draft guidance provides recommendations for sponsors regarding the use of real-world data in conducting studies. It also addresses the challenges and limitations associated with the use of these data and provides recommendations to overcome them. The purpose of this article is to provide a brief overview of key aspects of the FDA's guidance on the use of electronic health record data in regulatory decision making.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Rare or orphan diseases belong to one of the most severe groups of diseases. At the same time, early and accurate diagnosis of such diseases is a serious problem for general practitioners, pediatricians and therapists. The article discusses the possibilities of using machine learning methods, including artificial intelligence, to improve the diagnosis of rare diseases. Information is provided on various models developed by both international experts and Russian researchers.