RESOLUTION
On September 19, 2024, in Moscow (Russian Federation), the V annual scientific-practical conference with international participation "RWD/RWE. Possible and Real" were organized and held. The theme of the conference brings together leading experts in RWD and RWE fields. The participants of the conference discussed the research tools of RWD/RWE, the confirmed value of RWE in modern medicine, legislation, and global perspectives worldwide, including the Russian Federation and the EAEU. A total of 28 reports were heard at the conference. Based on the results of the conference, a Resolution was developed, the text of which we offer you to familiarize yourself with.
METHODOLOGY
Relevance. Observational studies (OS) play a key role in the healthcare system because they provide real-world data (RWD). Unlike randomized controlled trials (RCTs), such studies better reflect routine medical practice. This makes them especially valuable for decision-making aimed at improving the quality and accessibility of medical care.
The objective of this article was to analyze key points related to OS data preparation derived from RWD for further evidence synthesis. This work was conducted within a review of asymptomatic hyperuricemia (AH) and was intended to lead to the consensus among rheumatologists on the management patterns of patients with AH in the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods. This article examined and described the process of preparing OS data for evidence synthesis.
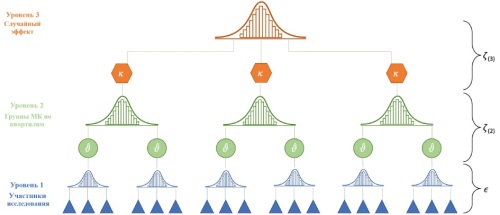
Results. The data analysis revealed significant measures of the efficacy and safety of the medical interventions and pivotal aspects of preparing OS data for subsequent evidence synthesis. We employed a number of techniques to overcome discrepancies in the presentation of the included OS data, including subgroup pooling, unloading of mean and standard deviations from medians and quartiles, and the synthesis of mean values in quartiles from a lognormal distribution via multiple replications. Urinary acid levels based on available OS were calculated using the Hunter-Schmidt estimator. Changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) across quartiles were pooled in accordance with the sequential Cochrane community approach or recalculated using community delta unloading equations in instances where GFR values fell within the observation time boundaries.
Findings. The results confirmed the importance of preparing appropriate OS data for evidence synthesis. OS provides valuable data for practical use when considering clinical factors and evaluating long-term treatment outcomes.
Conclusions. Consequently, observational studies and their preparations can provide a more comprehensive and precise understanding of the efficacy of medical interventions and enhance the quality and accessibility of care for all patients.
Relevance. The main treatment option for urinary tract infections is antimicrobials, which are selected empirically accord ing to local epidemiologic data. In recent years, a new source of data on antimicrobial resistance, which is based on real-world data (RWD) analysis.
Objective. To study the distribution and structure of antimicrobial resistance of urinary infection pathogens in the Kalinin grad region according to RWD.
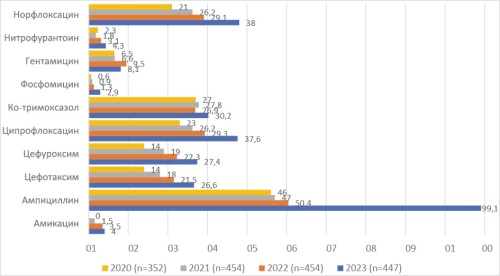
Methods. The results of bacteriological studies on urine samples collected from inhabitants of the Kaliningrad region, which were performed in the INVITRO laboratory, were analyzed. The total number of bacteriologic studies in 2020 was 2251, in 2021–2765, in 2022–2544 and in 2023–2373 samples. Urine samples were collected from the outpatient clinic.
Results. The study population was predominantly female (80.0 % to 89.9 %). The suspected causative agent was detected in 26.8 % — 29.3 % of patients. The most frequently isolated pathogen was E. coli (58.7 %–63.1 %). Other bacteria of the order Enterobacterales were isolated much less frequently: Klebsiella pneumoniae (6.4 %–9.7 %), Enterobacter spp. (0.9 %–2.4 %), Proteus spp. (0.3 %–2.9 %), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (0.7 %–3.7 %). Among Gram-positive bacteria, Enterococci (6.3 %–7.8 %), Streptococcus agalactiae (1.6 %–3.6 %), and Staphylococcus saprophyticus (1.4 %–2.8 %) were most frequently isolated. Growth of resistance to almost all antimicrobial agents was noted. At the same time, fosfomycin (2.9 % of strains are resistant), nitrofurantoin (4.3 %), and amikacin (4.0 %) remain the most active E. coli-resistant drugs.
Conclusion. The use of RWD to assess local antimicrobial resistance can be a valuable source of information, reflecting the true picture of antimicrobial resistance in a certain region and complementing the available information provided by other methods.
The results of identifying new risks for pharmacovigilance systems and databases in Russia, including the Roszdravnadzor's web-based pharmacovigilance system, are presented. The lack of information in the database on pharmacovigilance of the Eur asian Economic Union and problems with updating programs and using alternative systems were noted. Changes in RWD/RWE information in global pharmacovigilance over the past 5 years.
Objectives. Identification of new risks associated with pharmacovigilance systems and databases in Russia. Materials and methods. The materials were obtained by interviewing 138 pharmacovigilance specialists and from regula tory legal acts, publications, computerized systems, and databases through open and authorized access. Sociological methods were used: survey in Telegram-group «Pharmacovigilance CIS» in October 2024 and information-analytical methods: user testing, review, and analysis of Russian and foreign systems and programs, including databases for pharmacovigilance, regu latory documentation, and bibliography.
Results. 17 % of pharmacovigilance specialists use exclusively Russian software in their computerized systems and data bases, 29 % use only foreign software, 35 % use both Russian and foreign software, and 19 % find it difficult to classify their systems and programs as domestic or foreign. The results of user testing indicate that there are problems and risks with access ing Roszdravnadzor’s web-based pharmacovigilance system via foreign browsers in current versions of Windows, Android, MacOS, iOS, and Unix operating systems. The unified pharmacovigilance database of the Eurasian Economic Union as of No vember 5, 2024, contains no public access notifications. The composition of data in the global database, VigiBase, has changed over 5 years: the largest number of cases now relates to COVID-19 vaccines. Russian data were not included in EudraVigilance and VigiBase (from October 10, 2020), which does not allow them to be considered in the global analysis.
Conclusion. New potential risks for computerized systems and databases for pharmacovigilance in Russia have been iden tified — loss of data and reduction in the quality of analysis.
HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
Background. The incidence of generalized meningococcal infection (GFMI) is increasing in the Russian Federation. However, meningococcal infection (MI) excludes into the National Immunization Program (NIP) yet. The burden of calculating GFMI as a function of disease severity is important for understanding its social significance.
Objective. To evaluate the socioeconomic burden of GFMI in the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted from the perspective of the healthcare system and society as a whole using a modeling method for children and adults, taking into account the following costs: 1) direct medical costs: emergency medical care, inpatient and outpatient treatment, and rehabilitation treatment; 2) direct non-medical costs: payment of dis ability pensions and temporary disability (TD); 3) indirect costs: loss of gross domestic product (GDP) and economic losses as a result of premature death from MI in childhood. When calculating costs, 4 models of patients were developed based on expert assessment and identified based on disease severity, the need to stay in the intensive care unit, and the volume of rehabilitation measures and treatment. The calculation horizon was 1year.
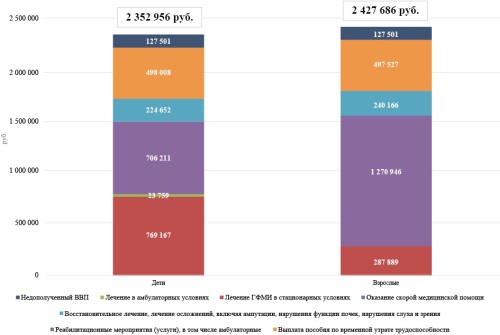
Results. The total annual socioeconomic burden of GFMI in the target population of 611 patients (data 2023) of various ages was 1.395 billion RUR. Direct medical costs accounted for 72.8 % of the total costs. Most direct medical costs (933 007 981 RUR) were expenses for rehabilitation measures (505 967 674 RUR) and treatment of GFMI under inpatient conditions (304 190 032 RUR). Indirect medical expenses (TD) accounted for 24 % of the total burden, amounting to 311 443 579 RUR. The weighted average cost per patient in the pediatric population was 2,35 mln RUR per year, of which 769 167 RUR were spent on hospital treatment (32.6 % of total costs). The weighted average cost per adult patient is 2,4 mln RUR per year, of which 1, mln RUR accounted for rehabilitation measures (52.3 % of total costs or 70.5 % of direct medical costs equal to 1,80 mln RUR per year per patient). Economic losses due to premature death of a child (0–14 years old) designed for the considered cohort amounted to 70.96 mln RUR.
Conclusion. While maintaining morbidity dynamics, the total cost of GFMI over 3 years will amount to more than 4 bln RUR. The burden calculation shows the significant social significance of this disease and indicates the need for preventive measures at the national level, such as MI inclusion in the NIP. These measures should make it possible to reduce future expenses and to save labor.