ACTUAL REVIEW
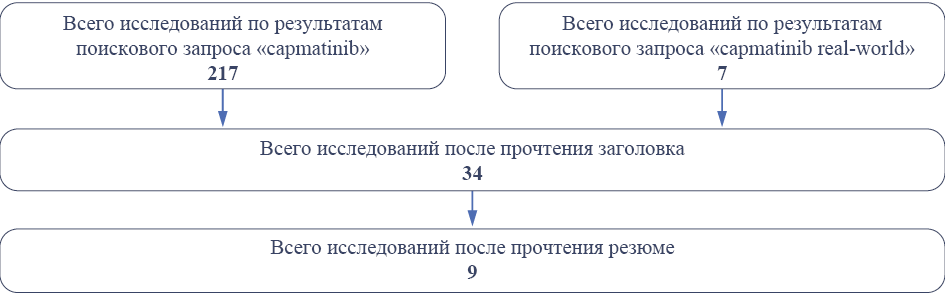
Lung cancer occupies a leading position in the structure of mortality from malignant neoplasms, so in 2022, mortality from lung cancer was 31.66 per 100,000 population, in 2022, 44,981 patients were registered with a diagnosis of lung cancer for the first time in their life, the one-year mortality rate is 44.8 %. One of the genes involved in the development of lung cancer tumor cells is the MET gene, in which several different mutations have been found, but the deletion of exon 14 is the most common. This mutation occurs in 3–4 % of cases of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), is an independent factor in poor prognosis, and is associated with short overall survival. The drug capmatinib was first registered in 2020 specifically for treating NSCLC in the presence of a deletion of exon 14 in the MET gene. This study systematically reviewed the real-world clinical practice studies of capmatinib in NSCLC.
Introduction. Thromboembolic complications represent several pathological processes and remain a common complication of most surgical interventions and one of the leading causes of failure in free flap transplantation. Thrombosis at the anastomotic site is not only the most common cause of failure in microsurgical operations, but it is also one of the factors leading to impaired circulation in free flaps and, as a consequence, the ineffectiveness of the performed treatment.
Objective. The current review discusses the numerous ways of thromboprophylaxis that can play a role in ensuring flap survival after a well-performed surgery.
Materials and methods. The initial search identified approximately 10,000 articles published from 1980 to September 2024. After reviewing the titles and abstracts, articles analyzing non-pharmacological methods of thromboprophylaxis, in which there are no indications of specific drugs, no indications of the outcomes of the experiment or clinical trial, as well as articles published in other languages or full-text versions of which are not published in the public domain were excluded. In total, 34 full-text articles were analyzed in the review.
Results. This article considers drugs whose pharmacological action is aimed at preventing the formation of blood clots or their destruction (antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, fibrinolytics) and drugs that indirectly, through other mechanisms of action, can reduce the likelihood of blood clots in transplanted flaps — dextran, prostacyclin, and nitric oxide. None of the analyzed studies indicated that the use of any group of drugs can lead to improved prognosis and reliably reduce the number of perioperative thrombotic complications.
Conclusion. Higher-level studies are needed to examine the clinical use of antithrombotic drugs in microsurgery; however, given the low failure rate in current practice, a well-designed study, with all procedures performed by surgical teams with relevant experience and patients randomized to treatment groups, is needed to achieve adequate power.
DRUG UTILIZATION RESEARCH
Objective. To determine the characteristics of pharmaceutical care for patients with headache in specialized neurology clinics.
Materials and methods. Questionnaire survey of clinic patients with the integrated ID–Migraine test using a validated questionnaire (from August to October 2023 inclusive) by a continuous sampling method, statistical processing of the results. Descriptive statistics and parametric and nonparametric methods were used in the statistical processing. The initially established level of statistical significance was considered to be at least 95 % at p <0.05.
Results. The study was conducted until 100 completed questionnaires were received. There was a high prevalence of women (84.0 %), mostly older than 40 years (68.1 %, n=94), and the average age of patients was 49.4±1.5 years. Migraine as a cause of headache was stated by 21.0 % of patients, and 38.9 % of patients answered positively to two or more questions of the ID–Migraine test (n=98), which may indicate the presence of migraine. Self-medication is widespread among patients (78.0 %), with 71.0 % considering it necessary to consult a physician only in case of prolonged headache that does not go away with analgesics. 63.0 % consider pharmacy as a specialized organization and pharmacists as highly qualified specialists who can qualitatively advise customers on drugs and symptoms, but should not diagnose and should not replace a physician (100.0 %). Also, the majority (72.0 %) believe that no pharmacist should be able to diagnose the type of headache based on symptoms and recommend drugs accordingly. Among the most important factors (on a 3‑point scale) influencing drug choice, clinic patients mentioned proven efficacy and safety (2.45±0.09), and prescribing physician (2.45±0.09). This indicates high compliance and trust of the clinic patients in the physician. The results of the questionnaire revealed three «profiles » of patients, the basis of which being fundamentally different attitudes toward pharmacists, pharmacies and physicians: neutral (loyal to pharmacies and pharmacists), highly loyal (to pharmacies and pharmacists), and loyal to the physician.
Conclusion. Patients in clinics may be represented by different subgroups with specific characteristics, needs, preferences, and, accordingly, different strategies of pharmaceutical care. This highlights the need for an individualized approach to communication between the pharmacists and each patient, considering the specificity of their needs and expectations.
Relevance. Myocardial infarction (MI) remains one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. The high prevalence of this atherosclerosis-associated disease is undoubtedly associated with insufficient prevention of cardiovascular diseases, including due to insufficient use of statins. This article highlights the problem of evaluating the use of statins as a means of primary and secondary cardiovascular prevention using the example of myocardial infarction from a sample of patients in the Siberian region.
Objective. To evaluate the frequency of statin use in patients before the onset of primary and recurrent type 1 myocardial infarction.
Materials and methods. The open continuous cross-sectional study included 294 patients selected from the local registry of acute coronary syndrome, treated at the 1st cardiology department of the Novosibirsk State Clinical Hospital No. 1 in 2021–2023. A multifactorial logistic regression model was used to assess the effect of various factors on the use of statins at the prehospital stage.
Results. It was found that in the subgroup of primary MI, the frequency of statin use was 21.8 %, and in the subgroup of repeated MI, the frequency was 38.6 %. An analysis of the factors associated with statin use revealed a statistically significant association with repeated myocardial infarction, OR 2.26 (1.29–3.99), and with dyslipidemia, OR 1.81 (1.02–3.25). Other factors: hypertension, diabetes mellitus type 2, obesity, atrial fibrillation, left ventricular ejection fraction, creatinine levels, age and gender. They have not reached the level of significance. The doses of the drugs corresponded to clinical recommendations; in 70 % of cases, atorvastatin was used, and in 30 %, rosuvastatin was used. Among the patients taking statins, many (more than 2/3 of the patients) did not reach the target values of LDL cholesterol.
Conclusions. The present study demonstrates insufficient frequency, intensity and duration of statin therapy among patients hospitalized with primary and recurrent type 1 myocardial infarction, and this indicates a poor state of primary and secondary prevention of this preventable cardiovascular event.
Objective. To assess the volume and structure dynamics of antidepressant consumption in the Russian Federation (RF).
Materials and methods. Data on the sales of medicines belonging to the ATX class N06A (antidepressants) were downloaded from the IQVIA database in the period 2019–2024. Selected those mentioned in the current Russian clinical guidelines for use in patients with neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders (ICD code F40‑F48). The estimated number of patients who received a one-year course of antidepressants, as well as the number of DDDs/1000 inhabitants per day in each of the follow-up years, was calculated.
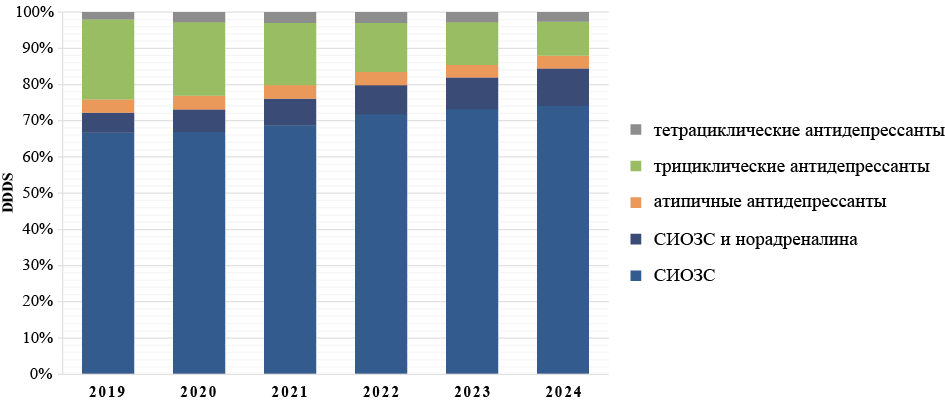
Results. In the period 2019–2024, sales of antidepressants more than doubled in the RF: 200 million were sold in 2019, while about 500 million DDDs in 2024, which corresponds to 3.8 in 2019 and 9.4 DDDs/1000 inhabitants per day in 2024. The estimated number of patients who received a one-year course of antidepressants increased from 570,000 in 2019 to 1.38 million in 2024. The predominant sales channel throughout the observation period was retail sales, which accounted for 84 % in 2019 to 94 % in 2024 of the total sales in each of the observation years. SSRIs (primarily sertraline and escitalopram) accounted for most sales (up to 75 %) throughout the follow-up. Regional sales correlated with the size of the region’s population.
Conclusions. The expansion of the practice of using antidepressants in the RF requires careful collection of safety data both as part of the analysis of the national Pharmacovigilance database and as part of real clinical practice research.
OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
Observational study, crucial for understanding complex real-world phenomena, often suffers from poor data detectability and reproducibility. The MINERVA (Metadata for Data Discovery and Research Reproducibility in Observational Studies) project in Europe aimed to address these issues by developing and implementing reliable metadata standards and practices.