ACTUAL REVIEW
This article examines the challenge of bridging the "valley of death" in medical research and development (R&D) — a critical phase where many promising projects fail to advance to implementation and commercialization. This study analyzes organizational, legal, financial, economic, and methodological obstacles that hinder the translation of scientific discoveries into practical healthcare. This study focuses on the Russian legislative framework governing scientific research and analyzes the socioeconomic impact of adopting new medical technologies based on international experience. The article highlights a paradox: despite substantial investments in medical R&D, many projects fail due to difficulties in assessing their innovative potential, inadequate coordination among stakeholders, and stringent regulatory requirements. The authors propose potential solutions, such as fostering public-private partnerships, streamlining regulatory processes, advancing translational medicine, and implementing knowledge management systems. This article is intended for researchers, regulators, pharmaceutical industry representatives, and healthcare policymakers seeking to accelerate the adoption of medical innovations.
DRUG SAFETY
Introduction. Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) are used for medical purposes and do not require external storage and transportation. In the context of supply chain risk management, the publication is currently not relevant. These gateways are transported in a closed or non-frozen environment. Cryopreservation is the gold standard for the storage and transportation of living cells; however, its impact on the quality of medicinal products remains unclear. Some safety issues are strictly addressed on an individual basis when transporting frozen cells: the materials used to produce the main container and the cryoprotective reagents used. In this regard, the development of approaches to managing logistics risks for ATMP is relevant for developing the ATMP market in Russia.
Objective. To develop criteria for assessing contractors and service providers in the market for circulating high-tech medicinal products by holders of registration certificates.
Materials and methods. The materials were the results of the analysis of the world and own scientific data and regulatory documents in the relevant field. General scientific methods, system and process approaches, and methods for analysis, synthesis, and extrapolation were applied.
Results. Risks arising in drug supply logistics chains were identified. The criteria for selecting a service provider for the transportation of ATMP and other heat-labile medicinal products for the holder of a registration certificate, applied to reduce the risks associated with logistics chains, are substantiated. Potential suppliers of transportation services for medicines are recommended based on the developed criteria. This study substantiates the development of recommendations for ATMP risk management for investors, pharmaceutical manufacturers and distributors for ATMP production and implementation localization.
Conclusions. Risks arising during the transportation and storage of medicinal products requiring special storage conditions were investigated. The risk management of medicinal products at the distribution stage requires a comprehensive approach.
Introduction. This work is a continuation of the study of the safety of drug therapy in clinical trials, within the framework of which a decision-making algorithm based on the quantitative integral analysis of adverse events (AE) was proposed. It is necessary to test the developed algorithm in clinical practice on various groups of drugs. Vaccines for the active prevention of viral hepatitis A were selected for testing. The results obtained can form the basis for assessing the capability of the method in forming a forecast for the development of adverse reactions during vaccination.
Objective. Determination of the effectiveness and promising areas of application of individualized integral analysis of adverse events based on the results of clinical trials using vaccines for the active prevention of viral hepatitis A as an example.
Materials and methods. Individualized integral assessment of AE was performed using an algorithm, the main stages of which are presented in detail in the previous works of the authors, based on the results of clinical studies of the vaccine’s safety and immunogenicity against viral hepatitis A, conducted in accordance with the regulatory and ethical requirements of the Russian Federation. At the stage of determining the weighting factors, an expert survey was conducted using the hierarchy analysis method to assess the importance of individual characteristics of adverse events. Mathematical and statistical analyses of individualized integral assessments were performed using validated software. To solve the problem of assessing the information content and discriminatory significance of gender-age and clinical-laboratory indicators for the purpose of subsequent prediction of the possible development of adverse health deviations, the GDA module — General Discriminant Analysis Models — was used.
Results. In the process of implementing the main stages of the quantitative integral analysis of AE based on the results of a clinical study of vaccines for the prevention of viral hepatitis A at the system-organ and organism levels, data were obtained indicating that there is no need for additional expert assessment or repeated study of this drug. The frequency of adverse reactions for individual organs and systems established in this study was higher than the level for similar vaccines listed in the study protocol. Using discriminant analysis, the information content of individual gender-age and clinical-laboratory indicators obtained during the screening of volunteers was assessed to separate groups of individuals with increased and moderate sensitivity to the introduction of vaccines for the prevention of viral hepatitis A. Only 8 of 37 indicators made a statistically significant contribution to the separation of the analyzed groups. The indicators being studied had low infor- mation content, which indicates insufficient specificity of the features among the screening examination data for predicting the development of adverse health conditions. The overall level of discrimination of the analyzed groups based on the screening examination data of volunteers was approximately 79 %. The proportion of correct classification of the group of individuals with increased sensitivity to drug introduction was 63 %.
Conclusions. The method of quantitative integral analysis of adverse events developed and tested on the example of vaccines for the prevention of viral hepatitis A has shown the potential for its use in identifying individuals with increased individual sensitivity during vaccination based on initial gender-age, demographic, and clinical-laboratory parameters. Further studies are planned to be conducted on pooled data on adverse reactions during the use of vaccines with similar organ-specific and systemic disorders during clinical trials and according to the automated information system "Pharmacovigilance", as well as by expanding the methods of mathematical and statistical data processing, including neural network analysis.
COHORT STUDIES
Relevance. The introduction of CDK4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib) into clinical practice has significantly improved the treatment outcomes of patients with metastatic HR+/HER2-breast cancer. However, the lack of reliable predictors of therapy response limits the possibilities of personalization of treatment. Leukopenia, the most common hematological complication of CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy, not only reflects the degree of myelosuppression but also serves as an indirect indicator of the pharmacodynamic effect associated with the suppression of bone marrow cell proliferation through a mechanism similar to the targeted effect on the tumor. Despite individual studies demonstrating a potential link between leukopenia degree and therapy effectiveness, data from actual clinical practice remain contradictory and insufficiently systematized.
Objective. This study retrospectively examined the possible predictors of CDk4/6 inhibitor effectiveness in clinical practice.
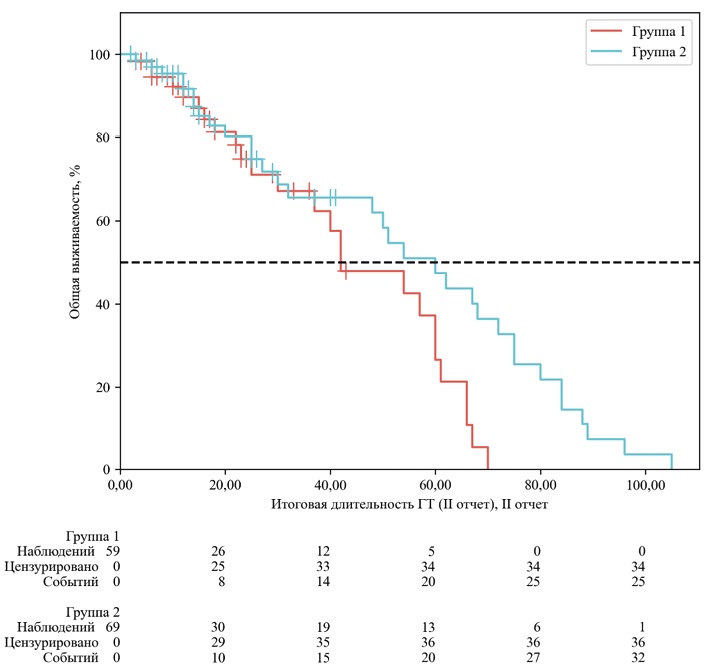
Materials and methods. A retrospective, multicenter analysis of data from 170 HR+/HER2-breast cancer patients treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib or ribociclib) in five cancer centers in Siberia and the Far East from 2019 to 2020 was conducted. The patients were stratified into two groups based on the maximum degree of toxicity according to CTCAE v5.0: group 1 (leukopenia G0–1, n=81) and group 2 (leukopenia G≥2, n=89). The primary and secondary endpoints were overall survival (S) and progression-free survival (PFS).
Results. Patients in group 2 (leukopenia G≥2) showed a statistically significant increase in median OS compared with group 1 (leukopenia G0-1): 60.0 months (95 % CI: 32.0–72.0) versus 42.0 months (95 % CI: 30.0–60.0), respectively (risk ratio [HR] 0.64; 95 % CI: 0.42–0.97; p=0.034). In the analysis of progression-free survival (PFS), an improvement trend was observed in group 2 (median 68.0 vs 60.0 months), but it did not reach statistical significance (p >0.05).
Conclusion. In a real-world study, the development of grade 2 and higher leukopenia during CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy was associated with improved OS. These data confirm that the degree of myelosuppression can serve as a valuable and readily available predictive biomarker of treatment effectiveness.
QUALITY OF LIFE
Actuality. Third molar problems have a multifactorial negative impact on patients’ quality of life (QoL), affecting the medical, psychological, social, and economic aspects of life. A comprehensive assessment of this impact is a pressing task for optimizing dental care and improving patients’ quality of life.
Objective. This study conducted a systematic analysis of modern data on the impact of third molars on various aspects of QoL by assessing the influence of medical, psychological, social, and economic factors.
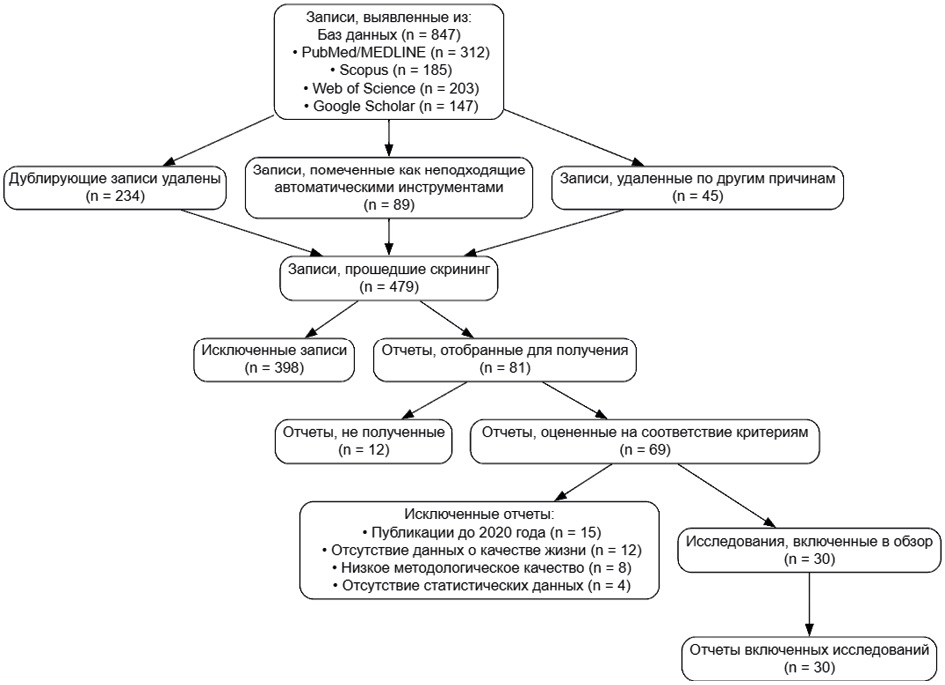
Materials and methods. A systematic review of the scientific literature was conducted from 2020 to 2025 using the PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases. The inclusion criteria included publications published after 2020 containing statistical data on the impact of third molars on patients’ lives. Content analysis was used to systematize the data using validated QOL assessment tools, including OHIP-5, PSQI, AIS, and ESS.
Results. It was found that 52 % of patients with third molar problems suffer from sleep disorders, with an insomnia score of 5.56±3.23 points on the AIS scale. The risk of developing caries of adjacent teeth increases by 1.39 times and root resorption by 6.51 times. The overall QoL score of patients with impacted molars is 0–14 points versus 0–11 in the control group (p<0.05). The economic analysis showed that conservative management is the costliest approach compared with prophylactic extraction. The strategy of preserving asymptomatic third molars provide cost savings for national health care systems.
Conclusions. Third molars have a significant negative impact on patients’ QoL through sleep disorders, dental complications, and psychosocial dysfunction. The constructed model of multifactorial impact allows predicting the need for various types of dental care and optimizing the health care system’s economic costs for third molar pathology treatment.
RESOLUTION
This article presents the outcomes of the VI Annual Scientific and Practical Conference with international participation "RWD/RWE. Possible and Real", which focused on the use of Real-World Data (RWD) and Real-World Evidence (RWE) in healthcare. The event facilitated a comprehensive analysis of the current state of RWD/RWE regulatory frameworks, methodological approaches, and practical applications in the Russian Federation and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). Key systemic limitations were identified, including gaps in legislation, the lack of standardized methods for data collection and analysis, interoperability issues of information systems, and challenges related to confidentiality and personal data processing. A set of specific proposals and recommendations aimed at improving the regulatory framework, developing in- frastructure for working with RWD, integrating such data into health technology assessment processes, developing clinical guidelines, and implementing innovative drug supply models. Harmonizing approaches at the EAEU level, data standardization, and creating secure mechanisms for researchers and developers to access anonymized medical information are of particular importance. The resolution materials are intended for legislative and executive authorities, regulators, medical and scientific organizations, pharmaceutical industry representatives, and patient communities.